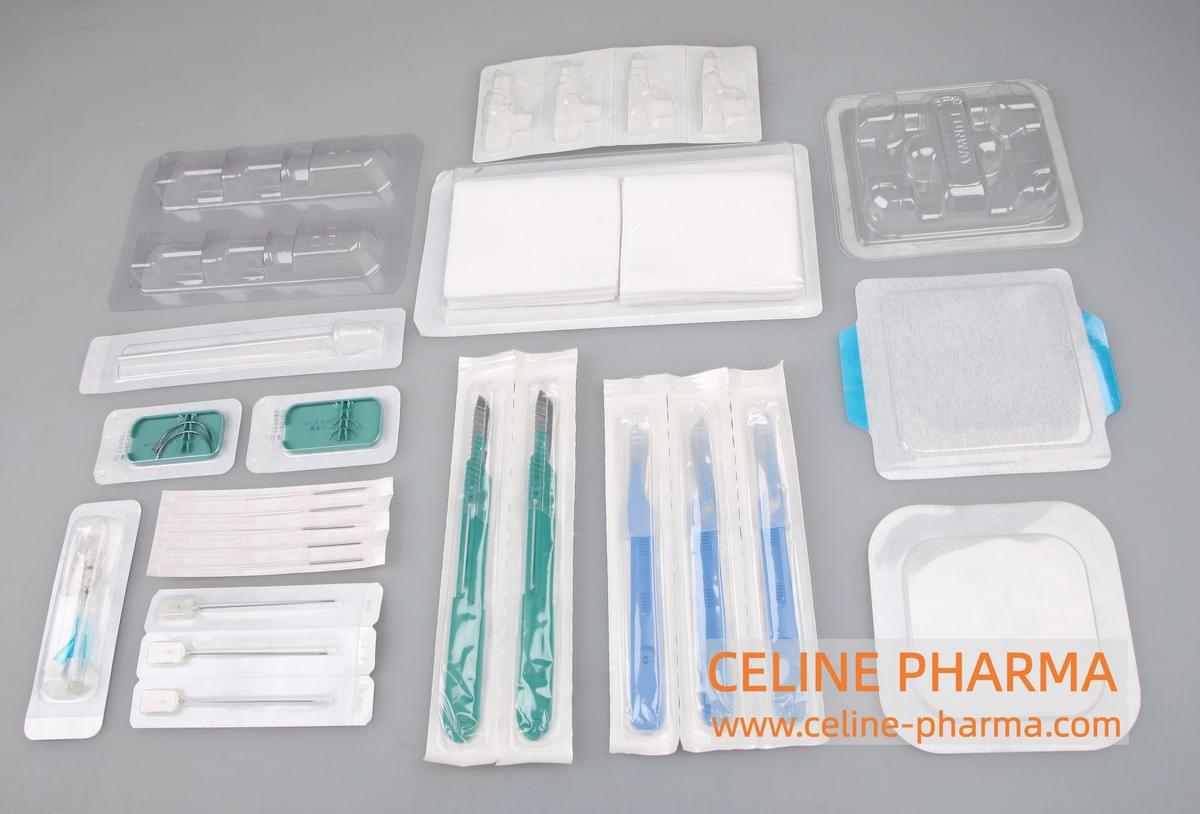
The "Dialysis Paper Soft Blister Packaging Machine" is a very important and widely used specialized equipment in the field of medical device packaging. It precisely combines the advantages of two packaging forms, creating a unique packaging structure.
Core Definition and Use
This is a packaging equipment designed specifically for medical devices that require terminal sterilization. The packaging it produces consists of two parts:
- Soft Plastic Blister: Formed from a heat-formable plastic film (such as PET/PE) through heating and vacuum forming, used to contain and fix the device, providing three-dimensional protection.
- Dialysis Paper Lid: As the top sealing material of the packaging, its porous structure allows sterilization factors such as ethylene oxide (EO) and steam to penetrate, while blocking microorganisms.
Main Uses: Packaging various irregularly shaped, fragile, or medical devices that require precise positioning and need to be protected from shaking during transportation.
Typical products include:
- High-end syringe and needle combinations
- Surgical instruments (such as scissors, forceps, needle holders)
- Orthopedic implant kits
- Catheter connectors, valves, and other plastic components
- Minimally invasive surgical instruments
- Diagnostic reagent components
Core Advantages:
- Excellent Protection: The blister cavity provides customized three-dimensional fixation for the device, preventing collision, crushing, and displacement, offering far superior protection compared to flat paper-plastic bags.
- Proven Sterilization Reliability: Using long-proven medical-grade dialysis paper as the sterilization channel, the sterilization effect is stable and reliable, and is a recognized standard in the industry.
- Good Display and Functionality: The product is clearly visible in the transparent blister, and the dialysis paper surface is convenient for writing and attaching labels. The packaging has a certain rigidity, making it easy to handle and open.
- Barrier Properties: The plastic blister layer effectively prevents moisture, providing a physical barrier for the device.
Detailed Explanation of Operation (Fully Automatic Roll-to-Roll Process)
Its operating principle is a combination of traditional blister forming technology and the sterile sealing requirements of medical devices. The process is highly automated and precise.
Step 1: Material Feeding and Preparation
- Forming Film Unwinding: The roll of the lower soft plastic composite film (such as PET/PE, APET/PE) is installed on the main unwinding shaft. This film has the characteristic of being stretchable and formable after heating.
- Dialysis Paper Unwinding: The roll of medical dialysis paper is mounted onto an unwinding shaft. The basis weight, air permeability, and strength of the dialysis paper must meet the standards.
- Product Feeding: The medical devices to be packaged (such as syringes) are precisely oriented and arranged using a vibratory feeder, conveyor belt, or robot, and then fed into the filling station.
Step 2: Heating and Blister Forming
- The lower soft plastic film is pulled through a heating device and uniformly heated to its precise thermoforming temperature (usually lower than that used for pharmaceutical-grade rigid PVC).
- The heated and softened film immediately enters the forming mold station. The mold closes, and the film is stretched into concave blisters that perfectly match the shape of the medical devices through vacuum forming (the main method) or a combination of positive pressure blowing. Each cavity is custom-designed to securely hold the product.
Step 3: Cooling and Product Filling
- The formed blister strip passes through a cooling zone (water cooling or air cooling) for shaping.
- High-precision robotic arms or pusher systems place the devices one by one into the corresponding blister cavities. A vision inspection system often monitors this station to ensure no missing parts and correct positioning.
Step 4: Dialysis Paper Covering and Heat Sealing (The Most Critical Technical Step)
- The roll of dialysis paper is pulled and laid flat over the formed blister strip already filled with devices.
- In the heat sealing mold, heat sealing is performed under precisely controlled temperature, pressure, and time.
- Technical Key: The heat melts the coating on the edges of the plastic blister, combining with the hot-melt adhesive layer on the back of the dialysis paper (or through the resin of the dialysis paper itself) to form a continuous, uniform, and strong sealing edge. This process must ensure a secure seal while absolutely not damaging the microporous breathable structure of the dialysis paper.
Step 5: Coding and Die Cutting
- In the sealing edge area, a thermal transfer printer prints product batch numbers, expiration dates, sterilization indicators, and other information.
- Finally, a precision die-cutting mold cuts the continuous packaging strip into individual packages. The cutting must be clean and precise, without producing paper or plastic burrs.
Step 6: Online Inspection and Output
- The finished products are output via a conveyor belt and can be equipped with a vision inspection system to automatically check for seal integrity, print quality, and the presence of foreign objects or product damage.
- Qualified products are automatically counted and collected into sterilization trays or breathable bags, ready for the sterilization process.
Summary
The dialysis paper soft plastic blister packaging machine is one of the mainstays in the field of sterile packaging for medical devices. Through the mature process of "thermoforming of soft plastic film to create a protective cavity" + "heat sealing of dialysis paper to provide a reliable sterilization channel," it perfectly balances product protection, sterilization reliability, and cost control.
Its operation essentially involves the highly complex combination of "precision vacuum forming of flexible materials" and "heat sealing of paper-plastic composites that are extremely sensitive to temperature." When selecting this type of equipment, it is essential to conduct rigorous process validation with the supplier to determine the optimal material combination (forming film/dialysis paper) and heat sealing parameters best suited for your product, ensuring that the packaging's seal strength, sterile barrier performance, and sterilization adaptability fully comply with regulatory requirements.